The HydraI data have already been described in detail in the previous
chapters.
In summary, the photometry (Chapter ![]() -
-![]() )
is based on observations made in April 1994
with the Danish 1.5 meter telescope at ESO,
La Silla, equipped with the DFOSC instrument.
Global photometric parameters for 64 galaxies in Gunn r and Johnson B
and 22 galaxies in Johnson U
are listed in
Table
)
is based on observations made in April 1994
with the Danish 1.5 meter telescope at ESO,
La Silla, equipped with the DFOSC instrument.
Global photometric parameters for 64 galaxies in Gunn r and Johnson B
and 22 galaxies in Johnson U
are listed in
Table ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() )
for Gunn r, and
Table
)
for Gunn r, and
Table ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() )
for Johnson B and U.
The spectroscopy (Chapter
)
for Johnson B and U.
The spectroscopy (Chapter ![]() ) is in part from the above-mentioned
observing run, and in part from JFK95b and J97.
In addition data from Lucey & Carter (1988) were used for three galaxies.
Global spectroscopic parameters for 51 galaxies
are listed in Table
) is in part from the above-mentioned
observing run, and in part from JFK95b and J97.
In addition data from Lucey & Carter (1988) were used for three galaxies.
Global spectroscopic parameters for 51 galaxies
are listed in Table ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() ).
The number of galaxies with both photometry and spectroscopy is 45;
for details see
Table
).
The number of galaxies with both photometry and spectroscopy is 45;
for details see
Table ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() ).
The photometry is estimated to be complete to
).
The photometry is estimated to be complete to
![]() ,
corresponding to
,
corresponding to
![]() .
(The calculation of distance dependent quantities is explained below.)
Of these galaxies, 80% have spectroscopy.
The sample covers the central part of the cluster, with a maximum center
distance of 57', corresponding to 1.3 Mpc.
This sample is larger than any other complete sample of HydraI
galaxies used for investigations of the FP.
.
(The calculation of distance dependent quantities is explained below.)
Of these galaxies, 80% have spectroscopy.
The sample covers the central part of the cluster, with a maximum center
distance of 57', corresponding to 1.3 Mpc.
This sample is larger than any other complete sample of HydraI
galaxies used for investigations of the FP.
The Coma sample consists of 116 galaxies.
The data are
given in Appendix ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() ).
Of the 116 galaxies, D120 and D121 are omitted from the analysis, as their
photometric parameters are highly uncertain, due to the
small angular distance between the galaxies.
The photometry is from JF94.
We use the seeing corrected values that are given in JFK95a.
Velocity dispersions and
).
Of the 116 galaxies, D120 and D121 are omitted from the analysis, as their
photometric parameters are highly uncertain, due to the
small angular distance between the galaxies.
The photometry is from JF94.
We use the seeing corrected values that are given in JFK95a.
Velocity dispersions and
![]() values are
from the literature
(Davies et al. 1987;
Dressler 1987;
Lucey et al. 1991b;
Guzmán et al. 1992)
as compiled into a consistent system by JFK95b,
and from Jørgensen (1997b, in prep.).
values are
from the literature
(Davies et al. 1987;
Dressler 1987;
Lucey et al. 1991b;
Guzmán et al. 1992)
as compiled into a consistent system by JFK95b,
and from Jørgensen (1997b, in prep.).
![]() indices are available for a subsample of
44 of the galaxies (Jørgensen 1997b, in prep.) -
this subsample is not magnitude limited.
The photometry is estimated to be complete to
indices are available for a subsample of
44 of the galaxies (Jørgensen 1997b, in prep.) -
this subsample is not magnitude limited.
The photometry is estimated to be complete to
![]() corresponding to
corresponding to
![]() .
Of these galaxies, 93% have a measured
.
Of these galaxies, 93% have a measured ![]() and
and
![]() .
The sample covers the central
.
The sample covers the central
![]() of the cluster,
with a maximum center distance of 47', corresponding to 1.7 Mpc.
This sample is larger than any other complete sample of Coma
galaxies used for investigations of the FP.
For comparison, the Coma sample used in JFK96 has 79 galaxies.
Their Coma sample is a subsample of the Coma sample used in this study.
of the cluster,
with a maximum center distance of 47', corresponding to 1.7 Mpc.
This sample is larger than any other complete sample of Coma
galaxies used for investigations of the FP.
For comparison, the Coma sample used in JFK96 has 79 galaxies.
Their Coma sample is a subsample of the Coma sample used in this study.
Table ![]() also list typical measurement errors for the different quantities.
These are all based on external comparisons.
The exception is
also list typical measurement errors for the different quantities.
These are all based on external comparisons.
The exception is
![]() ,
where the typical uncertainties are based on comparisons between
data from different observing runs using different instruments,
but not from other authors.
The HydraI and Coma samples do not have enough galaxies in common
with e.g. Faber (1994) to enable an actual external comparison.
The errors in
,
where the typical uncertainties are based on comparisons between
data from different observing runs using different instruments,
but not from other authors.
The HydraI and Coma samples do not have enough galaxies in common
with e.g. Faber (1994) to enable an actual external comparison.
The errors in
![]() and
and
![]() are highly anti-correlated,
with a linear correlation coefficient r of about -0.95.
The uncertainty on a function
are highly anti-correlated,
with a linear correlation coefficient r of about -0.95.
The uncertainty on a function
![]() is calculated as
is calculated as
| = | 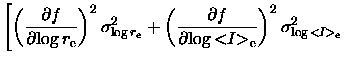 |
||
![$\displaystyle + \left. 2 r \sigma_{\log{r_{\rm e}}}\sigma_{\log{< \hspace{-1pt}...
...og{< \hspace{-3pt} I \hspace{-3pt}>_{\rm e}}}} \right)
\right]^{1/2}
\enspace ,$](img544.gif) |
(7.1) |
The distance dependent quantities (absolute magnitudes,
![]() in kpc,
and cluster center distances in Mpc)
were calculated as follows.
Coma was assumed to be at rest with respect to the CMB frame
at
in kpc,
and cluster center distances in Mpc)
were calculated as follows.
Coma was assumed to be at rest with respect to the CMB frame
at
![]() ,
and the
distance to HydraI relative to Coma was calculated from the
FP zero point difference
,
and the
distance to HydraI relative to Coma was calculated from the
FP zero point difference
![]() (Eq.
(Eq. ![]() ).
).
![]() and q0 = 0.5
was assumed.
The formulas used are given in
Sect.
and q0 = 0.5
was assumed.
The formulas used are given in
Sect. ![]() (p.
(p. ![]() ).
The derived redshift for HydraI (Eq.
).
The derived redshift for HydraI (Eq. ![]() ) is
) is
![]() .
For comparison, the CMB redshift is
.
For comparison, the CMB redshift is
![]() .
The distance moduli for Coma and HydraI are
.
The distance moduli for Coma and HydraI are
| (7.2) |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Properties of E and S0 Galaxies in the Clusters HydraI and Coma
Master's Thesis, University of Copenhagen, July 1997![]()
Bo Milvang-Jensen (milvang@astro.ku.dk)