



Next: 5.3 Parameters Quantifying the
Up: 5. Global Photometric Parameters
Previous: 5.1 Effective Parameters
At the
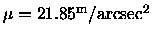 isophote in Gunn r
we determined the ellipticity,
isophote in Gunn r
we determined the ellipticity,
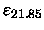 .
JF94 found that
.
JF94 found that
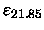 was better determined than
was better determined than
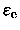 for
their data and therefore used
for
their data and therefore used
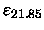 in their analysis.
They also found that
in their analysis.
They also found that
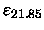 was close to the maximum ellipticity for disky galaxies
for their Coma sample.
For disky galaxies, the ellipticity varies substantially with radius,
see e.g. the
was close to the maximum ellipticity for disky galaxies
for their Coma sample.
For disky galaxies, the ellipticity varies substantially with radius,
see e.g. the
 profile for R266 on p.
profile for R266 on p. ![[*]](http://www.astro.ku.dk/Icons/latex2html-96.1/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
In Fig.
.
In Fig. ![[*]](http://www.astro.ku.dk/Icons/latex2html-96.1/cross_ref_motif.gif) we compare
we compare
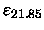 with
with
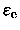 for the 64 HydraI galaxies in our sample.
It is seen that the two ellipticities in most cases agree well,
although there is significant intrinsic scatter in the relation.
For the analysis of our HydraI data,
it will not be important whether we use
for the 64 HydraI galaxies in our sample.
It is seen that the two ellipticities in most cases agree well,
although there is significant intrinsic scatter in the relation.
For the analysis of our HydraI data,
it will not be important whether we use
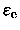 or
or
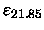 as measure of the ellipticity.
The two very deviating
galaxies at
as measure of the ellipticity.
The two very deviating
galaxies at
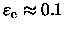 and
and
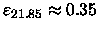 are
R225 and R327,
both SB0 galaxies with an ellipticity that varies rapidly with radius.
This can be seen from the
are
R225 and R327,
both SB0 galaxies with an ellipticity that varies rapidly with radius.
This can be seen from the
 profiles
on p.
profiles
on p. ![[*]](http://www.astro.ku.dk/Icons/latex2html-96.1/cross_ref_motif.gif) and p.
and p. ![[*]](http://www.astro.ku.dk/Icons/latex2html-96.1/cross_ref_motif.gif) -
the two galaxies both have
-
the two galaxies both have
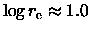 and
and
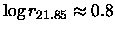 (with r in arcsec).
(with r in arcsec).




Next: 5.3 Parameters Quantifying the
Up: 5. Global Photometric Parameters
Previous: 5.1 Effective Parameters
Properties of E and S0 Galaxies in the Clusters HydraI and Coma
Master's Thesis, University of Copenhagen, July 1997

Bo Milvang-Jensen (milvang@astro.ku.dk)
![\begin{figure}% latex2html id marker 7773\makebox[\textwidth]{
\epsfxsize=\te...
...mp_global_phot}, p.~\pageref{tab:int_comp_global_phot})
are shown.
}\end{figure}](img400.gif)
![]()